Looking for about bios overclocking risks or learn about bios overclocking risks or discuss about bios overclocking risks or share about bios overclocking risks or ask about bios overclocking risks.
The process of overclocking refers to increasing the clock speed of computer hardware components, such as the central processing unit (CPU) or graphics processing unit (GPU), beyond their factory settings in order to attain enhanced performance. While overclocking can offer substantial performance gains, it also comes with its fair share of risks. In this article, we will explore some of the potential dangers associated with overclocking through the BIOS.
As clock speeds increase, so does the heat generated by the components. Overclocking can push the CPU or GPU to its limits, resulting in significantly higher temperatures. Excessive heat can cause stability issues, reduce the lifespan of the hardware, or even lead to permanent damage if not appropriately managed. It is crucial to have proper cooling measures, such as effective cooling fans and heatsinks, to mitigate the increased heat generated during overclocking.
When overclocking, higher clock speeds often require increased voltage levels. However, pushing the voltage too high can lead to instability and cause system crashes. Moreover, fluctuating voltage levels due to improper configurations can damage the hardware's delicate components and result in the loss of important data. Finding the right balance between clock speed and voltage is essential to prevent such risks.
Overclocking typically increases the stress placed on computer components. Running at higher clock speeds than intended can accelerate wear and tear, ultimately reducing the lifespan of the hardware. While modern components are designed to handle some level of overclocking, excessive overclocking or insufficient cooling can significantly diminish their durability. Users should be aware that overclocking may void their warranty and may result in having to replace components sooner than expected.
Pushing hardware beyond its intended limits can compromise system stability. Overclocking can cause system crashes, freezes, or random restarts. Instability issues can undermine productivity, cause data corruption, and lead to frustrating experiences. Users should be prepared to troubleshoot and fine-tune their overclocked settings to achieve stability and minimize such risks.
Overclocking through the BIOS requires detailed technical knowledge and careful consideration of multiple settings. Inexperience or mistakes during the process can result in unintended consequences. It is vital to have a good understanding of the hardware, adequate research on specific components, and reliable overclocking guides to avoid mishaps. User error can potentially lead to irreversible damage to the hardware, rendering it useless.
Bios overclocking can offer notable performance improvements, but it is crucial to be aware of the risks involved. Managing heat, voltage instability, reducing component lifespan, ensuring system stability, and avoiding user errors are key factors to consider before attempting any overclocking. While the risks exist, with proper precautions and understanding, users can safely enjoy the enhanced performance that overclocking can bring.
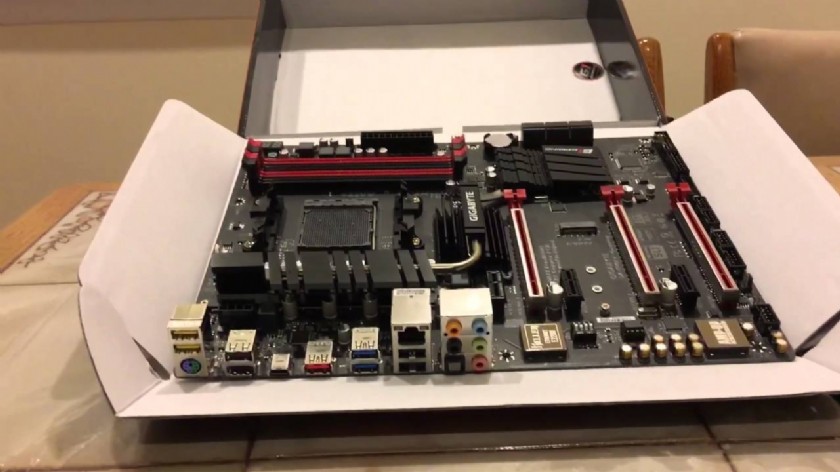

GIGABYTE GA-990FX-Gaming Motherboard Hardware InstallationThe motherboard contains numerous delicate electronic circuits and components which can beco
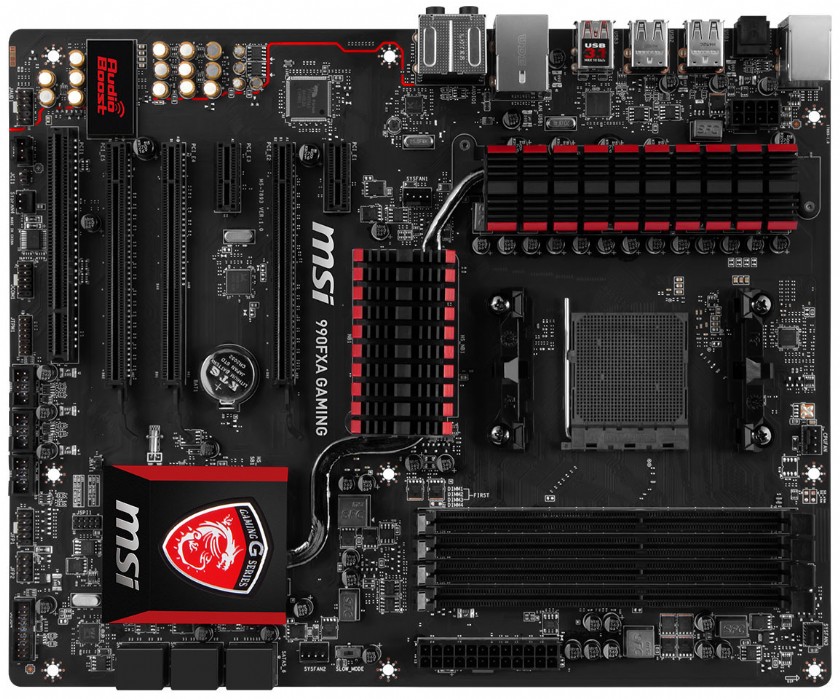
MSI 990FXA Gaming Motherboard SpecificationsCPU Support: Supports AMD FX/ Phenom II / Athlon II and Sempron processors for the AM3/ AM3+ socket.Hypert
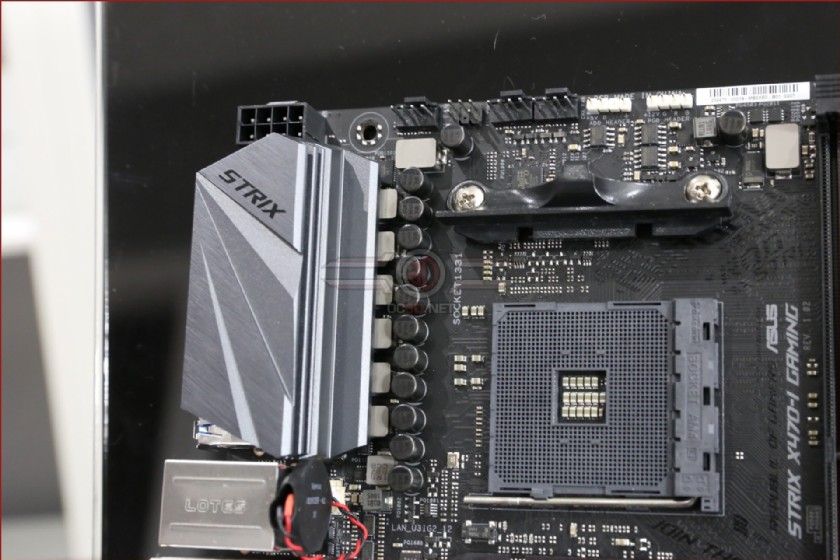

ASUS ROG STRIX X470-I GAMING Motherboard BIOS SetupBIOS (Basic Input and Output System) stores system hardware settings such as storage device configu
Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers
error '80004005'[MySQL][ODBC 8.0(w) Driver][mysqld-8.0.44]Can't find FULLTEXT index matching the column list
/ara.asp, line 492